what is a brinell hardness test|brinell hardness test chart : online sales History Behind the Brinell Test. Let’s take a quick glance at the history behind the Brinell test. In 1900, Dr. J.A. Brinell invented this test. As an honor to him, the test named as a Brinell test. It is the oldest hardness test of all time. . web28 de jun. de 2021 · Maria Cândida estrela ensaio nu (Foto: Paola Guzman) A repórter Maria Cândida, de 50 anos de idade, estrelou um ensaio arrasador em que aparece nua, com o tema Nua com Propósito aos 50 anos. Em seu Instagram, nesta segunda-feira (28), ela postou uma série de cliques, feitos pelas lentes de Paola Guzman.
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBCursorblade 是一款光标射击游戏,您将扮演光标,与敌人一波接一波地战斗。. 结合武器和物品,打造独特的强大构建。. 斩击,闪避,升级,反复!. 类型: 射击 , 独立 , 街机 , 砍杀. 视角: 上帝视角. 版本: 发行版本 游戏本体. 模式: 单人. 主题: 动作. 光标之 .
Solar Radiation Simulation Tester–(wind cooling) fabrication
The Brinell hardness test is defined in ASTM E10 is used to calculate Brinell hardness of the metal. It is used on the metal having a rough surface and harsh texture. The Brinell hardness test is used to measure the .The Brinell hardness test method as used to determine Brinell hardness, is defined in ASTM E10. Most commonly it is used to test materials that have a structure that is too coarse or that have a surface that is too rough to be tested .
What is a Brinell Hardness Test? The Brinell hardness test is a widely recognized method for determining the hardness of various materials. It involves applying a constant load or .When measuring hardness using the Brinell method, a hardened steel or carbide ball of known diameter under a known load is forced into the material being tested. The diameter of the .History Behind the Brinell Test. Let’s take a quick glance at the history behind the Brinell test. In 1900, Dr. J.A. Brinell invented this test. As an honor to him, the test named as a Brinell test. It is the oldest hardness test of all time. .Brinell Hardness Tester holds significant importance in today's industrial landscape, where understanding material properties is crucial for ensuring product quality, reliability, and performance. This test reveals vital information .
Plastic slice Cutter fabrication
The Brinell hardness test is used to determine hardness and is done by forcing a hard steel or carbide ball indenter of a specified diameter onto the test metal surface under a specified load. This is followed by measuring the diameter of .The Brinell hardness testing method is used in various cases where large or rough surfaces, coarse-grained materials, or high loads are involved. It is particularly well-suited for testing the hardness of materials with relatively low hardness ranges, such as non-ferrous metals, castings, and softer steels.The Brinell hardness test is commonly used to determine the hardness of materials like metals and alloys. The test is achieved by applying a known load to the surface of the tested material through a hardened steel ball of known diameter. The diameter of the resulting permanent impression in the tested metal is measured and the Brinell Hardness . The Brinell hardness test is not suitable for very hard materials or hardened surface layers because the ball does not penetrate sufficiently into the material. Higher test loads are not the solution at this point, as this leads to deformation of the carbide ball. The flattening of the ball results in a larger indentation diameter and thus .
Brinell Hardness Test: Using a spherical indenter, this test determines the hardness by measuring the diameter of the indentation created by a known force. It’s suitable for materials with coarse grain structures or rough surfaces.In metallurgy: Testing mechanical properties .oldest of such tests, the Brinell hardness test, uses a 10-millimetre-diameter ball and a 3,000-kilogram load. Brinell hardness values correlate well with UTS.
The Brinell hardness test consists of applying a constant load, usually in the range 500–3000 . N, for a specified period of time (10–30 s) using a 5 or 10 mm diameter hardened steel or tungsten carbide ball on the flat surface of a work piece.. The Brinell hardness number (HB) .The Brinell hardness test is named after its inventor, Johan August Brinell. It involves applying a constant load or force to a spherical indenter made of hardened steel or carbide onto the surface of the material being tested. The indentation diameter is then measured optically. The Brinell hardness number (BHN) is calculated as the load .An alternative method is the Brinell hardness test, which uses a hardened steel (or tungsten carbide) ball indenter with a diameter D of, usually, 10 mm.This is applied under a load P of 500–3000 kg applied for 10–30 s.The diameter of the circular indentation d is measured in millimetres. The hardness number, (HB) is calculated using the following equation:The Brinell hardness test is an empirical indentation hardness test that can provide useful information about metallic materials. This information may correlate to tensile strength, wear resistance, ductility, and other physical characteristics of metallic materials, and may be useful in quality control and selection of materials. .
Brinell Hardness Test. The oldest of the hardness test methods in common use on engineering materials today is the Brinell hardness test. Dr. J. A. Brinell invented this test in Sweden in 1900. The Brinell test uses a desktop machine to apply a specified load to a hardened sphere of a specified diameter. The Brinell hardness number, or simply .Rockwell Hardness Test. Rockwell hardness test is one of the most common indentation hardness tests, that has been developed for hardness testing. In contrast to Brinell test, the Rockwell tester measures the depth of penetration of an indenter under a large load (major load) compared to the penetration made by a preload (minor load).
Brinell Hardness Tester is a rapid and accurate method to determine hardness value with ASTM E-10 compliance. Applying loads of up to 3.000 kgf, the Brinell test is ideal for castings and forgings.
The Brinell hardness test (HBW) serves as a crucial scale for quantifying material hardness, defined in ASTM E10 and BS EN ISO 6506-1 standards. This test involves pressing a Brinell indenter against a test specimen under a . When the Brinell hardness test cannot be used, such as when the material’s HB value is greater than 450 or the sample size is too small, the Rockwell hardness test is used instead. This test involves pressing either a . 4.1 The Brinell hardness test is an indentation hardness test that can provide useful information about metallic materials. This information may correlate to tensile strength, wear resistance, ductility, or other physical characteristics of metallic materials, and may be useful in quality control and selection of materials. Hardness testing methods: Rockwell, Brinell and microhardness Heat treating has evolved into a highly complex, precise process that improves characteristics of metal parts. A critical component of quality heat treating is employing the correct hardness testing method to show manufacturers their parts achieve design requirements.
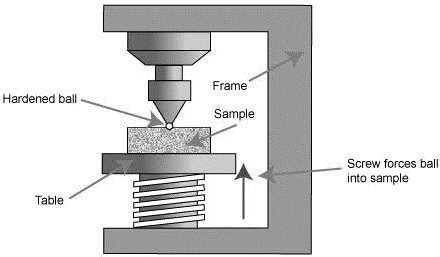
The Brinell hardness test uses a spherical indenter which is pressed, by a precisely controlled force – most commonly 3,000 kgf – into the material being measured. The force builds between two and eight seconds then is sustained for several more to ensure that the indentation is a plastic deformation (see footnote). The diameter of the . The Brinell hardness test consists of applying a constant load or force, usually between 187.5 and 3000Kgf, for a specified time (from 10 – 30 seconds) typically using a 2.5 or 10mm diameter tungsten carbide ball (see schematic in the image to your right – Figure 23.3).While the Brinell hardness test is widely used in the industry today, some features which make it unique are worth mentioning. Firstly, it enjoyed standardization before any other method was standardized which also accounts for why it is widely used. It is also the preferred accurate method for rough and coarse-grained surfaces that otherwise .
The Brinell hardness test uses a spherical indenter, while the Rockwell hardness test uses either a diamond cone or steel ball indenter. Another difference is the amount of force applied to the surface of the material. The Brinell hardness test typically uses a higher load than the Rockwell hardness test.The test provides numerical results to quantify the hardness of a material, which is expressed by the Brinell hardness number – HB. The Brinell hardness number is designated by the most commonly used test standards (ASTM E10-14[2] and ISO 6506–1:2005) as HBW (H from hardness, B from brinell and W from the material of the indenter, tungsten .
Brinell Hardness Testing: Involves applying a known load to the surface of the test sample via a hardened steel or carbide ball; Vickers Hardness Testing: Utilises an optical measuring system to measure the area of the impression; Knoop Hardness Testing: Employs a diamond penetrator to impress a sample;The Brinell hardness test is used to measure and inspect materials with rough surfaces such as forgings and casting because you cannot use other methods to inspect them. This is because this method uses a large indenter (usually 10 mm) which averages the rough surface of the test piece for better results. It is also used to assess the hardness .In the Brinell hardness test, an optical method, the size of indentation left by the indenter is measured. In contrast to the likewise optical Vickers method,which involves a pyramid-shaped indenter being pressed into a specimen, the Brinell method uses a spherical indenter.
brinell hardness tester diagram
brinell hardness test theory
brinell hardness test pdf
Resultado da Assistir Earthsounds Temporada 1 no Netflix, FoxPlay, MEO, etc.? Veja onde assistir todos os episódios online agora.
what is a brinell hardness test|brinell hardness test chart